What is Apex Batch Class in Salesforce?
In Salesforce development, handling large data volumes efficiently is a common challenge. This is where the Apex Batch Class comes into play. A Batch Apex allows developers to process millions of records asynchronously without hitting governor limits.
Unlike a trigger or synchronous class, a Batch Apex job runs in chunks (batches) of records, making it perfect for long-running or data-intensive operations. Salesforce automatically manages the execution so that resources are optimized and performance remains stable.
Key Benefits of Using Apex Batch Class
- Handles Large Data Volumes – Processes records in manageable chunks.
- Scalable & Efficient – Perfect for enterprises dealing with big data.
- Asynchronous Execution – Runs in the background without interrupting users.
- Error Handling – Provides clear control over failures in each batch.
- Flexibility – Can be scheduled, monitored, and chained with other jobs.
Core Concepts of Batch Apex
The Role of Database.Batchable Interface
Every Apex Batch Class must implement the Database.Batchable interface. This interface defines how Salesforce processes batches of records.
The Three Mandatory Methods
- Start() – Collects the records to be processed.
- Execute() – Runs on each batch of records.
- Finish() – Performs final operations after all batches are processed.
Batch Size Considerations
- Default size: 200 records per batch.
- Can range between 1 to 2,000 records.
- Choose based on complexity and performance needs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing an Apex Batch Class
Setting Up a Batch Class in Salesforce
A typical batch class starts with:
global class mySampleBatchApex implements Database.Batchable<SObject> {
// We hardcode the desired value here in a static variable.
private static final String TARGET_RATING = 'Hot';
// 1) start():
public Database.QueryLocator start(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
// WHY: Excluding already‑'Hot' reduces DML and avoids needless row locking.
return Database.getQueryLocator([
SELECT Id, Rating
FROM Account
WHERE Rating = NULL OR Rating != :TARGET_RATING
]);
}
// 2) execute(): bulk‑safe update of the current scope.
public void execute(Database.BatchableContext bc, List<Account> scope) {
if (scope.isEmpty()) return; // If scope is empty better not to execute: no work, no DML.
List<Account> accountsToUpdate = new List<Account>(); // create a list for all acccounts to be updated
for (Account a : scope) {
// WHY: Double‑checking.
if (a.Rating != TARGET_RATING) {
a.Rating = TARGET_RATING;
accountsToUpdate.add(a); // add to the above created list
}
}
if (!accountsToUpdate.isEmpty()) {
// WHY: allOrNone=false so one failure doesn't abort the whole chunk.
Database.update(accountsToUpdate, /* allOrNone */ false); // performing database.update outside the for loop.
}
}
// 3) finish(): good place for logging or notifications; kept simple here.
public void finish(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
System.debug(LoggingLevel.INFO, 'mySampleBatchApex finished. All Accounts set to \'' + TARGET_RATING + '\'.');
}
}
Running/Executing a Batch Job from Developer Console Anynomous window:
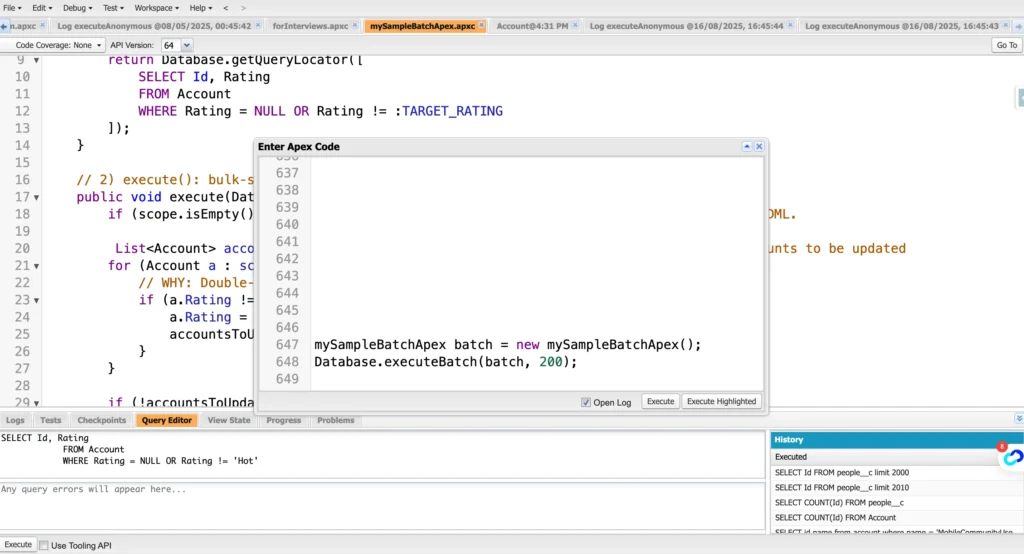
mySampleBatchApex batch = new mySampleBatchApex();
Database.executeBatch(batch, 200);
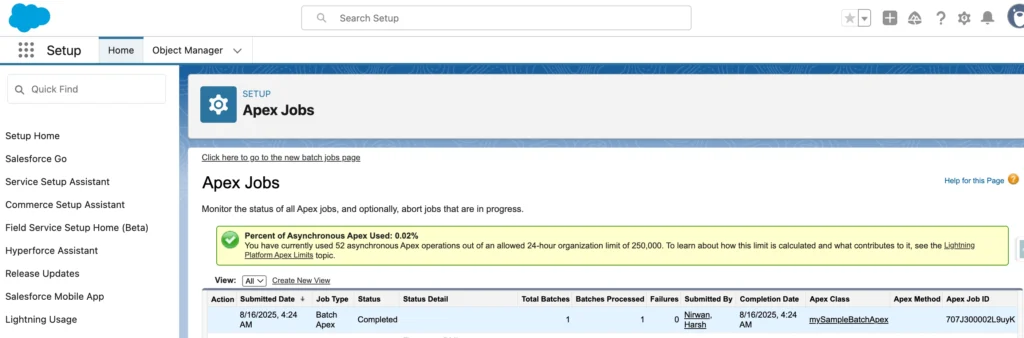
Monitoring and Debugging
- Go to Setup → Apex Jobs to track status.
- Use System.debug() for troubleshooting.
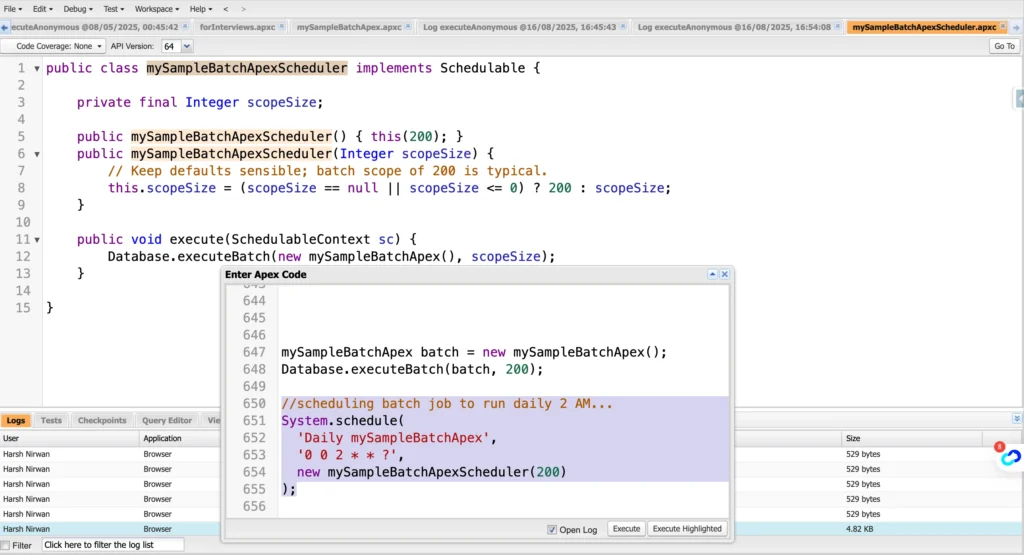
Now, lets schedule this batch job to run daily at 2 AM
Create another scheduler apex class ->
public class mySampleBatchApexScheduler implements Schedulable {
private final Integer scopeSize;
public mySampleBatchApexScheduler() { this(200); }
public mySampleBatchApexScheduler(Integer scopeSize) {
// Keep defaults sensible; batch scope of 200 is typical.
this.scopeSize = (scopeSize == null || scopeSize <= 0) ? 200 : scopeSize;
}
public void execute(SchedulableContext sc) {
Database.executeBatch(new mySampleBatchApex(), scopeSize);
}
}Running/Scheduling a Batch Job from Developer Console Anynomous window:
As we can see that we have provided the ‘cron expression’ to set the timings and executed the highlighted code to schedule our apex batch job.
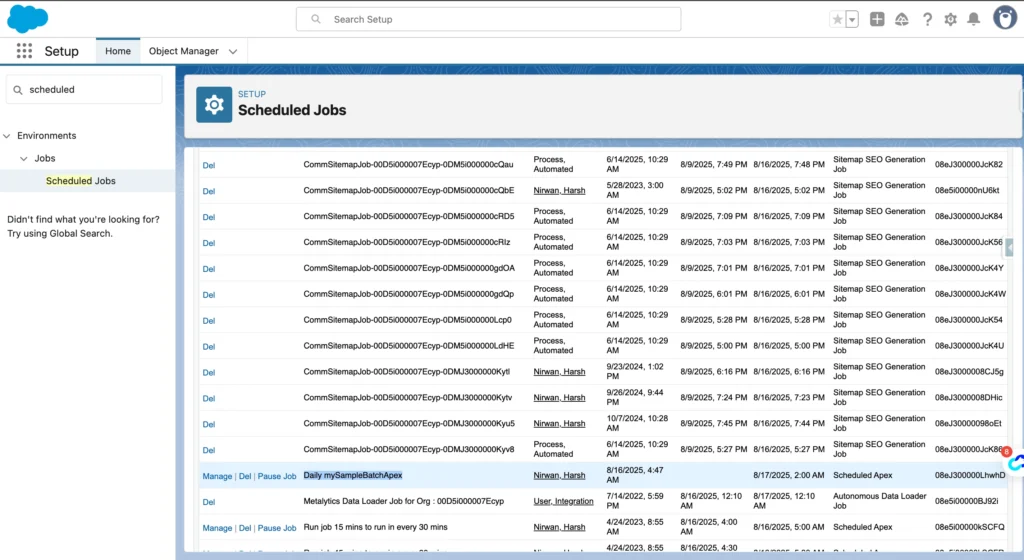
Monitoring and Debugging
- Go to Setup → Scheduled Jobs to track status.
Real-World Use Cases of Apex Batch Class
- Data Cleansing & Deduplication – Remove duplicates in millions of records.
- Mass Updates – Recalculate fields like revenue or territory assignments.
- Integrations – Sync large data sets with external systems.
Best Practices for Apex Batch Class
- Use selective SOQL queries to avoid unnecessary records.
- Implement try-catch blocks for error handling.
- Break down jobs into smaller batches for better efficiency.
- Always test in a sandbox before running in production.
Apex Batch Class vs Queueable Apex vs Future Methods
FeatureBatch ApexQueueable ApexFuture Methods
Records Handled Millions Limited Very Limited
Async Execution Yes Yes Yes
Chaining Yes Yes No
Monitoring Yes Yes No
✅ Use Batch Apex for heavy data jobs.
✅ Use Queueable Apex for medium jobs needing chaining.
✅ Use Future Methods for lightweight background jobs.
Common Challenges and How to Solve Them
- Governor Limits → Use efficient queries.
- Debugging Large Jobs → Add logging inside execute().
- Data Locking → Avoid updates on the same record in parallel jobs.
FAQs about Apex Batch Class
Q1. What is the maximum number of batch jobs I can run in Salesforce?
You can have up to 5 queued or active batch jobs at a time.
Q2. Can I call a batch class from another batch?
Yes, but use Queueable Apex for chaining batch jobs effectively.
Q3. What is the maximum batch size in Salesforce?
The maximum batch size is 2,000 records.
Q4. How do I monitor batch jobs?
Navigate to Setup → Apex Jobs for job details.
Q5. Is Apex Batch Class synchronous or asynchronous?
It is always asynchronous.
Q6. Can I test batch classes in Apex test methods?
Yes, use Test.startTest() and Test.stopTest() to simulate batch execution.
Conclusion:
Why Every Developer Should Master Apex Batch Class
The Apex Batch Class is one of the most powerful tools Salesforce offers for handling large datasets. By mastering its structure, best practices, and real-world applications, developers can build efficient, scalable, and error-resistant applications. Whether you’re cleaning data, syncing with external systems, or performing massive recalculations, Batch Apex is your go-to solution in 2025 and beyond.
🔗 Learn more from Salesforce’s official docs: Salesforce Apex Batch Apex Guide
Please follow me on linkedin : Harsh Veer Nirwan
Please do check oy other articles as well : https://thetechnologyfiction.com/linear-search-and-sorting-algorithm-in-salesforce-using-apex-2025/




